非常欢迎大家参与这个linux格式化命令问题集合的探讨。我将以开放的心态回答每个问题,并尽量给出多样化的观点和角度,以期能够启发大家的思考。
1.linux系统硬盘怎么格式化
2.linux 系统怎么磁盘格式化
3.linux如何彻底格式化ssd?
4.格式化u盘linux格式化u盘linux
5.Linux里面mkfs命令作用是什么?
linux系统硬盘怎么格式化
LVM将一个或多个硬盘的分区在逻辑上集合,相当于一个大硬盘来使用,当硬盘的空间不够使用的时候,可以继续将 其它 的硬盘的分区加入其中,这样可以实现磁盘空间的动态管理,相对于普通的磁盘分区有很大的灵活性。那么你知道linux系统硬盘怎么格式化吗?我带来了linux系统硬盘格式化的具 体操 作过程,下面大家跟着我一起来学习一下吧。linux系统硬盘怎么格式化
分区与格式化
先用fdisk分区,分区完成后再用mkfs格式化并创建文件系统,挂载,磁盘就能使用啦。
分区的原理:
MBR:主引导扇区
主分区表:64bytes,最多只能分四个主分区,每个主分区的记录(相关信息,比如分区大小,位置)在主分区表里占14bytes。
如果要建多于四个的分区,就要拿出一个主分区做为扩展分区,再在扩展分区里面进行其它的分区操作。在 建扩展分区的时候会建立一张对应的扩展分区表,它记录了在这个扩展分区里的分区的相关信息;理论上它没有分区数量的限制,在扩展分区内部的分区叫做逻辑分区,如上图中的 /dev/hda5,/dev/hda6/,/dev/hda7
格式化原理:
在分好区后,分区里面是空的,没有任何东西。为了能让OS识别,就必须要向分区里写入相应格式的数据。比如windows的FAT32,NTFS;Linux的ext2,ext3,ext4(目前ext3格式的用的比较多,ext4还在实验之中,在新的Fedora上使用的就是ext4的文件系统)。
Windows/dos常用的分区工具:fdisk/partition magic/diskpart
Linux下常用的分区工具:
fdisk/sfdisk:命令行工具,各种版本和环境都能使用,包含在软件包util-linux中
diskdruid:图形化分区工具,只能在安装REDHAT系统时使用。
下面我们开始实验:
环境/工具:Fedora 14/256M内存卡;fdisk
第一步:fdisk
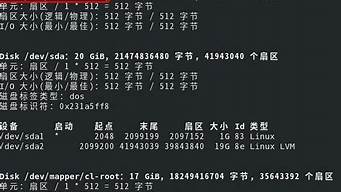
[root@novice ~]# fdisk -l /dev/sdb
Disk /dev/sdb: 254 MB, 254017536 bytes
8 heads, 61 sectors/track, 1016 cylinders, total 496128 sectors
Units = sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes
Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
Disk identifier: 0x00000000
Device Boot Start End Blocks Id System
[root@novice ~]# fdisk /dev/sdb
Command (m for help): #在输入上面的命令后会出现左边的提示,输入m就会得到一个帮助菜单,如下:
Command (m for help): m
Command action
a toggle a bootable flag
b edit bsd disklabel
c toggle the dos compatibility flag
d delete a partition
l list known partition types
m print this menu
n add a new partition
o create a new empty DOS partition table
p print the partition table
q quit without saving changes
s create a new empty Sun disklabel
t change a partition's system id
u change display/entry units
v verify the partition table
w write table to disk and exit
x extra functionality (experts only)
#help虽然是英文的,可都很简单,在这里不再解释。
#现在,我们正式开始分区的操作:
Command (m for help): n #新建分区
Command action
e extended
p primary partition (1-4)
#e/p分别对应扩展分区 /主分区;我们先分四个主分区,每个50M;然后再来增加主分区或扩展分区,看会出现怎样的状况,嘿嘿。
p #分区类型为主分区
Partition number (1-4, default 1): 1 #分区号,在这里我们依次选择1、2、3、4
First sector (2048-496127, default 2048): #指定分区的起始扇区,一般默认,按enter键即可。
Last sector, +sectors or +size{K,M,G} (2048-496127, default 496127): +50M #指定分区的终止扇区,根据前面的提示我们可以做出相应的选择+sectors 或 +size{K,M,G}
Command (m for help): p #用p打印出已建好的分区列表
Disk /dev/sdb: 254 MB, 254017536 bytes
8 heads, 61 sectors/track, 1016 cylinders, total 496128 sectors
Units = sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes
Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
Disk identifier: 0x00000000
Device Boot Start End Blocks Id System
/dev/sdb1 2048 104447 51200 83 Linux
#剩下的三个分区的建立操作同上
#分好四个主分区后的情况如下
Command (m for help): p
Disk /dev/sdb: 254 MB, 254017536 bytes
8 heads, 61 sectors/track, 1016 cylinders, total 496128 sectors
Units = sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes
Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
Disk identifier: 0x00000000
Device Boot Start End Blocks Id System
/dev/sdb1 2048 104447 51200 83 Linux
/dev/sdb2 104448 206847 51200 83 Linux
/dev/sdb3 206848 309247 51200 83 Linux
/dev/sdb4 309248 309298 25+ 83 Linux
#已经建好四个主分区啦,现在我们来看看如果再建主分区或是扩展分区的话会出现怎样的情况:
Command (m for help): n
You must delete some partition and add an extended partition first
#看到了吧,不能再建分区啦!要再建分区的话必须删除some分区,再新建一个扩展分区才行。
#现在,我们删掉一个主分区,来新建扩展分区
Command (m for help): d #删除分区
Partition number (1-4): 4 #选择要删除分区的分区号,我们选第四个
Command (m for help): p #打印,如下,四个分区变成了三个!
Disk /dev/sdb: 254 MB, 254017536 bytes
8 heads, 61 sectors/track, 1016 cylinders, total 496128 sectors
Units = sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes
Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
Disk identifier: 0x00000000
Device Boot Start End Blocks Id System
/dev/sdb1 2048 104447 51200 83 Linux
/dev/sdb2 104448 206847 51200 83 Linux
/dev/sdb3 206848 309247 51200 83 Linux
#新建一个扩展分区
#如果在没有建满三个主分的区的情况下建立扩展分区,相关选项会有些不同。
Command (m for help): n
Command action
e extended
p primary partition (1-4)
e
Selected partition 4
First sector (309248-496127, default 309248): #enter,默认
Using default value 309248
Last sector, +sectors or +size{K,M,G} (309248-496127, default 496127): #enter,默认,使用剩余空间
Using default value 496127
Command (m for help): p
Disk /dev/sdb: 254 MB, 254017536 bytes
8 heads, 61 sectors/track, 1016 cylinders, total 496128 sectors
Units = sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes
Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
Disk identifier: 0x00000000
Device Boot Start End Blocks Id System
/dev/sdb1 2048 104447 51200 83 Linux
/dev/sdb2 104448 206847 51200 83 Linux
/dev/sdb3 206848 309247 51200 83 Linux
/dev/sdb4 309248 496127 93440 5 Extended
#接下来,我们在新建的扩展分区里再新建两个逻辑分区,因为已经有了三个主分区,这里不会再显示是建立逻辑分区还是主分区的提示!
Command (m for help): n
First sector (311296-496127, default 311296): #enter
Using default value 311296
Last sector, +sectors or +size{K,M,G} (311296-496127, default 496127): +50M
Command (m for help): n
First sector (415744-496127, default 415744): #enter
Using default value 415744
Last sector, +sectors or +size{K,M,G} (415744-496127, default 496127): #enter
Using default value 496127
Command (m for help): p
Disk /dev/sdb: 254 MB, 254017536 bytes
8 heads, 61 sectors/track, 1016 cylinders, total 496128 sectors
Units = sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes
Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
Disk identifier: 0x00000000
Device Boot Start End Blocks Id System
/dev/sdb1 2048 104447 51200 83 Linux
/dev/sdb2 104448 206847 51200 83 Linux
/dev/sdb3 206848 309247 51200 83 Linux
/dev/sdb4 309248 496127 93440 5 Extended
/dev/sdb5 311296 413695 51200 83 Linux
/dev/sdb6 415744 496127 40192 83 Linux
#上面的列表,就是我们今天分区的成果啦!接下来保存退出,重启计算机,就可以进行下一步的mkfs操作啦!如果忘记了相关的操作命令,记得按m!!!
Command (m for help): w #保存
The partition table has been altered!
Calling ioctl() to re-read partition table.
Syncing disks.
另:在建好分区后,我们还可以更改相关分区的文件系统类型
#如,我们要把第二个主分区改成Linux下的交换分区,操作如下
Command (m for help): t #更改文件系统类型
Partition number (1-6): 2 #选择第二个分区
Hex code (type L to list codes): L #选择要更改的文件系统编码,可以按L来查看相关编码信息。
0 Empty 24 NEC DOS 81 Minix / old Lin bf Solaris
1 FAT12 39 Plan 9 82 Linux swap / So c1 DRDOS/sec (FAT-
2 XENIX root 3c PartitionMagic 83 Linux c4 DRDOS/sec (FAT-
3 XENIX usr 40 Venix 80286 84 OS/2 hidden C: c6 DRDOS/sec (FAT-
............
16 Hidden FAT16 64 Novell Netware af HFS / HFS+ fb VMware VMFS
17 Hidden HPFS/NTF 65 Novell Netware b7 BSDI fs fc VMware VMKCORE
18 AST SmartSleep 70 DiskSecure Mult b8 BSDI swap fd Linux raid auto
1b Hidden W95 FAT3 75 PC/IX bb Boot Wizard hid fe LANstep
1c Hidden W95 FAT3 80 Old Minix be Solaris boot ff BBT
1e Hidden W95 FAT1
Hex code (type L to list codes): 82 #查找到linux swap的编码为82
Changed system type of partition 2 to 82 (Linux swap / Solaris)
Command (m for help): p
..............
Device Boot Start End Blocks Id System
/dev/sdb1 2048 104447 51200 83 Linux
/dev/sdb2 104448 206847 51200 82 Linux swap / Solaris
/dev/sdb3 206848 309247 51200 83 Linux
/dev/sdb4 309248 496127 93440 5 Extended
/dev/sdb5 311296 413695 51200 83 Linux
/dev/sdb6 415744 496127 40192 83 Linux
#最后别忘了保存!如果你须要的话!
#扩展分区不能直接使用,逻辑分区只能建立在扩展分区上!
第二步:mkfs(mkfs时分区的格式最好与fdisk设定的分区格式一致,不然.......)
mkfs支持ext2 ext3 vfa msdos jfs reiserfs等文件系统。
用法1:mkfs -t
例: mkfs -t ext3 /dev/sdb2
用法2:mkfs.
例:mkfs,vfat /dev/sdb3
mke2fs支持ext2/ext3文件系统
用法:mke2fs [-j]
例:mke2fs -j /dev/sdb5
# 更多更具体的用法请参照相关命令的man手册
下面,接着实验:
例一
[root@novice ~]# mkfs -t ext3 /dev/sdb1
mke2fs 1.41.12 (17-May-2010)
Filesystem label=
OS type: Linux
Block size=1024 (log=0)
Fragment size=1024 (log=0)
Stride=0 blocks, Stripe width=0 blocks
12824 inodes, 51200 blocks
2560 blocks (5.00%) reserved for the super user
First data block=1
Maximum filesystem blocks=52428800
7 block groups
8192 blocks per group, 8192 fragments per group
1832 inodes per group
Superblock backups stored on blocks:
8193, 24577, 40961
Writing inode tables: done
Creating journal (4096 blocks): done
Writing superblocks and filesystem accounting information: done
This filesystem will be automatically checked every 34 mounts or
180 days, whichever comes first. Use tune2fs -c or -i to override.
例二:
[root@novice ~]# fdisk /dev/sdb
Command (m for help): t
Partition number (1-6): 6
Hex code (type L to list codes): L
0 Empty 24 NEC DOS 81 Minix / old Lin bf Solaris
1 FAT12 39 Plan 9 82 Linux swap / So c1 DRDOS/sec (FAT-
2 XENIX root 3c PartitionMagic 83 Linux c4 DRDOS/sec (FAT-
3 XENIX usr 40 Venix 80286 84 OS/2 hidden C: c6 DRDOS/sec (FAT-
4 FAT16 <32M 41 PPC PReP Boot 85 Linux extended c7 Syrinx
5 Extended 42 SFS 86 NTFS volume set da Non-FS data
6 FAT16 4d QNX4.x 87 NTFS volume set db CP/M / CTOS / .
7 HPFS/NTFS 4e QNX4.x 2nd part 88 Linux plaintext de Dell Utility
.........
Hex code (type L to list codes): 7
Changed system type of partition 6 to 7 (HPFS/NTFS)
Command (m for help): p
Disk /dev/sdb: 254 MB, 254017536 bytes
8 heads, 61 sectors/track, 1016 cylinders, total 496128 sectors
Units = sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes
Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
Disk identifier: 0x00000000
Device Boot Start End Blocks Id System
/dev/sdb1 2048 104447 51200 83 Linux
/dev/sdb2 104448 206847 51200 82 Linux swap / Solaris
/dev/sdb3 206848 309247 51200 83 Linux
/dev/sdb4 309248 496127 93440 5 Extended
/dev/sdb5 311296 413695 51200 83 Linux
/dev/sdb6 415744 496127 40192 7 HPFS/NTFS
Command (m for help): w
The partition table has been altered!
Calling ioctl() to re-read partition table.
Syncing disks.
[root@novice ~]# mkfs.ntfs /dev/sdb6
Cluster size has been automatically set to 4096 bytes.
Initializing device with zeroes: 100% - Done.
Creating NTFS volume structures.
mkntfs completed successfully. Have a nice day.
linux 系统怎么磁盘格式化
Linux下常用的分区工具:
fdisk/sfdisk:命令行工具,各种版本和环境都能使用,包含在软件包util-linux中
diskdruid:图形化分区工具,只能在安装REDHAT系统时使用。
第一步:fdisk
[root@novice ~]# fdisk -l /dev/sdb
Disk /dev/sdb: 254 MB, 254017536 bytes
8 heads, 61 sectors/track, 1016 cylinders, total 496128 sectors
Units = sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes
Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
Disk identifier: 0x00000000
Device Boot Start End Blocks Id System
[root@novice ~]# fdisk /dev/sdb
Command (m for help): #在输入上面的命令后会出现左边的提示,输入m就会得到一个帮助菜单,如下:
Command (m for help): m
Command action
a toggle a bootable flag
b edit bsd disklabel
c toggle the dos compatibility flag
d delete a partition
l list known partition types
m print this menu
n add a new partition
o create a new empty DOS partition table
p print the partition table
q quit without saving changes
s create a new empty Sun disklabel
t change a partition's system id
u change display/entry units
v verify the partition table
w write table to disk and exit
x extra functionality (experts only)
#help虽然是英文的,可都很简单,在这里不再解释。
#现在,我们正式开始分区的操作:
Command (m for help): n #新建分区
Command action
e extended
p primary partition (1-4)
#e/p分别对应扩展分区 /主分区;我们先分四个主分区,每个50M;然后再来增加主分区或扩展分区,看会出现怎样的状况,嘿嘿。
p #分区类型为主分区
Partition number (1-4, default 1): 1 #分区号,在这里我们依次选择1、2、3、4
First sector (2048-496127, default 2048): #指定分区的起始扇区,一般默认,按enter键即可。
Last sector, +sectors or +size{K,M,G} (2048-496127, default 496127): +50M #指定分区的终止扇区,根据前面的提示我们可以做出相应的选择+sectors 或 +size{K,M,G}
Command (m for help): p #用p打印出已建好的分区列表
Disk /dev/sdb: 254 MB, 254017536 bytes
8 heads, 61 sectors/track, 1016 cylinders, total 496128 sectors
Units = sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes
Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
Disk identifier: 0x00000000
Device Boot Start End Blocks Id System
/dev/sdb1 2048 104447 51200 83 Linux
#剩下的三个分区的建立操作同上
#分好四个主分区后的情况如下
Command (m for help): p
Disk /dev/sdb: 254 MB, 254017536 bytes
8 heads, 61 sectors/track, 1016 cylinders, total 496128 sectors
Units = sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes
Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
Disk identifier: 0x00000000
Device Boot Start End Blocks Id System
/dev/sdb1 2048 104447 51200 83 Linux
/dev/sdb2 104448 206847 51200 83 Linux
/dev/sdb3 206848 309247 51200 83 Linux
/dev/sdb4 309248 309298 25+ 83 Linux
#已经建好四个主分区啦,现在我们来看看如果再建主分区或是扩展分区的话会出现怎样的情况:
Command (m for help): n
You must delete some partition and add an extended partition first
#看到了吧,不能再建分区啦!要再建分区的话必须删除some分区,再新建一个扩展分区才行。
#现在,我们删掉一个主分区,来新建扩展分区
Command (m for help): d #删除分区
Partition number (1-4): 4 #选择要删除分区的分区号,我们选第四个
Command (m for help): p #打印,如下,四个分区变成了三个!
Disk /dev/sdb: 254 MB, 254017536 bytes
8 heads, 61 sectors/track, 1016 cylinders, total 496128 sectors
Units = sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes
Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
Disk identifier: 0x00000000
Device Boot Start End Blocks Id System
/dev/sdb1 2048 104447 51200 83 Linux
/dev/sdb2 104448 206847 51200 83 Linux
/dev/sdb3 206848 309247 51200 83 Linux
#新建一个扩展分区
#如果在没有建满三个主分的区的情况下建立扩展分区,相关选项会有些不同。
Command (m for help): n
Command action
e extended
p primary partition (1-4)
e
Selected partition 4
First sector (309248-496127, default 309248): #enter,默认
Using default value 309248
Last sector, +sectors or +size{K,M,G} (309248-496127, default 496127): #enter,默认,使用剩余空间
Using default value 496127
Command (m for help): p
Disk /dev/sdb: 254 MB, 254017536 bytes
8 heads, 61 sectors/track, 1016 cylinders, total 496128 sectors
Units = sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes
Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
Disk identifier: 0x00000000
Device Boot Start End Blocks Id System
/dev/sdb1 2048 104447 51200 83 Linux
/dev/sdb2 104448 206847 51200 83 Linux
/dev/sdb3 206848 309247 51200 83 Linux
/dev/sdb4 309248 496127 93440 5 Extended
#接下来,我们在新建的扩展分区里再新建两个逻辑分区,因为已经有了三个主分区,这里不会再显示是建立逻辑分区还是主分区的提示!
Command (m for help): n
First sector (311296-496127, default 311296): #enter
Using default value 311296
Last sector, +sectors or +size{K,M,G} (311296-496127, default 496127): +50M
Command (m for help): n
First sector (415744-496127, default 415744): #enter
Using default value 415744
Last sector, +sectors or +size{K,M,G} (415744-496127, default 496127): #enter
Using default value 496127
Command (m for help): p
Disk /dev/sdb: 254 MB, 254017536 bytes
8 heads, 61 sectors/track, 1016 cylinders, total 496128 sectors
Units = sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes
Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
Disk identifier: 0x00000000
Device Boot Start End Blocks Id System
/dev/sdb1 2048 104447 51200 83 Linux
/dev/sdb2 104448 206847 51200 83 Linux
/dev/sdb3 206848 309247 51200 83 Linux
/dev/sdb4 309248 496127 93440 5 Extended
/dev/sdb5 311296 413695 51200 83 Linux
/dev/sdb6 415744 496127 40192 83 Linux
#上面的列表,就是我们今天分区的成果啦!接下来保存退出,重启计算机,就可以进行下一步的mkfs操作啦!如果忘记了相关的操作命令,记得按m!!!
Command (m for help): w #保存
The partition table has been altered!
Calling ioctl() to re-read partition table.
Syncing disks.
另:在建好分区后,我们还可以更改相关分区的文件系统类型
#如,我们要把第二个主分区改成Linux下的交换分区,操作如下
Command (m for help): t #更改文件系统类型
Partition number (1-6): 2 #选择第二个分区
Hex code (type L to list codes): L #选择要更改的文件系统编码,可以按L来查看相关编码信息。
0 Empty 24 NEC DOS 81 Minix / old Lin bf Solaris
1 FAT12 39 Plan 9 82 Linux swap / So c1 DRDOS/sec (FAT-
2 XENIX root 3c PartitionMagic 83 Linux c4 DRDOS/sec (FAT-
3 XENIX usr 40 Venix 80286 84 OS/2 hidden C: c6 DRDOS/sec (FAT-
............
16 Hidden FAT16 64 Novell Netware af HFS / HFS+ fb VMware VMFS
17 Hidden HPFS/NTF 65 Novell Netware b7 BSDI fs fc VMware VMKCORE
18 AST SmartSleep 70 DiskSecure Mult b8 BSDI swap fd Linux raid auto
1b Hidden W95 FAT3 75 PC/IX bb Boot Wizard hid fe LANstep
1c Hidden W95 FAT3 80 Old Minix be Solaris boot ff BBT
1e Hidden W95 FAT1
Hex code (type L to list codes): 82 #查找到linux swap的编码为82
Changed system type of partition 2 to 82 (Linux swap / Solaris)
Command (m for help): p
..............
Device Boot Start End Blocks Id System
/dev/sdb1 2048 104447 51200 83 Linux
/dev/sdb2 104448 206847 51200 82 Linux swap / Solaris
/dev/sdb3 206848 309247 51200 83 Linux
/dev/sdb4 309248 496127 93440 5 Extended
/dev/sdb5 311296 413695 51200 83 Linux
/dev/sdb6 415744 496127 40192 83 Linux
#最后别忘了保存!如果你须要的话!
#扩展分区不能直接使用,逻辑分区只能建立在扩展分区上!
第二步:mkfs(mkfs时分区的格式最好与fdisk设定的分区格式一致,不然.......)
mkfs支持ext2 ext3 vfa msdos jfs reiserfs等文件系统。
用法1:mkfs -t
例: mkfs -t ext3 /dev/sdb2
用法2:mkfs.
例:mkfs,vfat /dev/sdb3
mke2fs支持ext2/ext3文件系统
用法:mke2fs [-j]
例:mke2fs -j /dev/sdb5
# 更多更具体的用法请参照相关命令的man手册
下面,接着实验:
例一
[root@novice ~]# mkfs -t ext3 /dev/sdb1
mke2fs 1.41.12 (17-May-2010)
Filesystem label=
OS type: Linux
Block size=1024 (log=0)
Fragment size=1024 (log=0)
Stride=0 blocks, Stripe width=0 blocks
12824 inodes, 51200 blocks
2560 blocks (5.00%) reserved for the super user
First data block=1
Maximum filesystem blocks=52428800
7 block groups
8192 blocks per group, 8192 fragments per group
1832 inodes per group
Superblock backups stored on blocks:
8193, 24577, 40961
Writing inode tables: done
Creating journal (4096 blocks): done
Writing superblocks and filesystem accounting information: done
This filesystem will be automatically checked every 34 mounts or
180 days, whichever comes first. Use tune2fs -c or -i to override.
第三部:挂载
挂载:mount
例:mount /dev/sdb1 /mnt /sdb1
卸载:umonut
例:umount /dev/sdb1
linux如何彻底格式化ssd?
linux格式化磁盘命令:mkfs。案例:格式化sda1分区[root@localhost beinan]#mkfs -t ext2 /dev/sda1 #将sda1磁盘分区格式化为ext2格式使用方式 : mkfs [-V] [-t fstype][fs-options] 说明 : 建立 linux 档案系统在特定的partition上参数 :device : 预备检查的硬盘 partition,例如:/dev/sda1;-V : 详细显示模式;-t : 给定档案系统的型式,Linux 的预设值为 ext2;-c : 在制做档案系统前,检查该partition 是否有坏轨;-l bad_blocks_file : 将有坏轨的block资料加到 bad_blocks_file 里面;block : 给定 block 的大小;-L:建立lable。
格式化u盘linux格式化u盘linux
Linux上格式化ssd硬盘操作步骤规格:240GPCIe接口ssd
关闭服务器加上新硬盘
启动服务器,以root用户登录
查看硬盘信息
#fdisk_l
创建新硬盘分区
跳过,我不需要ssd分区
格式化分区:
mkfs.ext4/dev/sdp
创建目录:
mkdir_p/mnt/sdp
挂载分区:
mount/dev/sdp/mnt/sdp
配置开机自动挂载
因为mount挂载在重启服务器后会失效,所以需要将分区信息写到/etc/fstab文件中让它永久挂载:
vim/etc/fstab
加上这样一行:
cat/etc/fstab查看
重启系统
Linux里面mkfs命令作用是什么?
Linux如何格式化磁盘啊?首先,格式化磁盘之前,确保你已经将磁盘正确分区。如果没有正确分区,那么磁盘格式化就会失败。针对磁盘的容量大小不同,有两种分区的方式,这里简单进行下讲解。
1.小于等于2T的磁盘,用fdisk进行分区。
2.大于2T以上的磁盘,用parted工具进行分区。
格式化命令为:以下两者任选其一即可
mkfs.ext4/dev/vdb1格式:mkfs.文件系统+分区名
mkfs-text4/dev/vdb1格式:mkfs-t文件系统+分区名
u盘格式化选哪个好?
1、金士顿u盘修复工具KingstonFormatUtility
金士顿官方出的专用修复工具,修复你的金士顿u盘,非常管用,遗憾的是只修金士顿的U盘,大家可以试试。
2、Mformat(u盘格式化软件)
是一款十分不错的U盘修复工具,可以修复U盘能检测到不能读取,能访问但字节为0,或者U盘容量无故变小等问题可以利该款工具进行格式化恢复。当你的MP3、U盘等移动存储设备遇到无法读取时,可以试试这个小工具。
在windows下如何格式化linux的分区?
其实不用重装,修复以下引导程序就能重新启动linux可以拿linuxlivecd光盘启动,运行boot-repiar,选择推荐修复,就可以了你要在windows下格式化linux分区,要先用分区软件,删除那个分区,然后重新分区,再格式化windows不能识别ext*格式的分区,所以windows下看不到
U盘启动安装linux时,U盘可以用哪种文件系统格式化?fat32或ntfs行不行?
用U盘安装Linux的话,必须用FAT32格式。如果u盘是NTFS格式的话,可以进入安装界面。但到选择开机引导程序界面后,则会提示错误。因为GRUB不支持NTFS格式,所以要用FAT32格式的。
监控u盘格式化成什么格式好?
格式化u盘有两种:FAT和NTFS格式
一.FAT32格式
FAT32格式兼容性相对好一些,几乎可以应对所有主流的操作系统(比如Windows、MacOS、Linux等),并且可以快速读写。但它的缺点是不能设置权限,安全等级较低;而且这个格式下的U盘最高只能支持4G以下的单个文件传输。
二.NTFS格式
NTFS格式使用最为广泛,可以对此格式的U盘进行权限设置,并且在互换性和实用性上远高于FAT3。NTFS格式在支持文件上最大可以拓展为256TB。需要使用到PE盘的用户,NTFS格式刷系统分区时也相对适用。
监控u盘格式化建议为NTFS格式。
Linux里面mkfs命令作用是什么?解答:
1.这是Linux系统下格式化磁盘的工具。
2.格式化的本质就是创建文件系统(组织和存取文件的机制)。
3.可以创建的文件系统有ext4(CentOS6),xfs(CentOS7)。
4.格式化命令:
好了,关于“linux格式化命令”的话题就到这里了。希望大家通过我的介绍对“linux格式化命令”有更全面、深入的认识,并且能够在今后的实践中更好地运用所学知识。